Discover comprehensive information for all aspects of sexual health and find resources and guidance to empower your sexual well-being.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition affecting men, often characterized by the inability to…
Discover comprehensive information for all aspects of sexual health and find resources and guidance to empower your sexual well-being.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition affecting men, often characterized by the inability to…
Sleep-related painful erection (SRPE) is a rare condition where people get painful erections while they’re…
Erectile dysfunction (ED) means having trouble getting or keeping an erection that’s good enough for…
Painful erections never indicate normalcy, and sometimes signal a medical emergency. Severe pain may necessitate…
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a condition that many men face at some point in their…
Feeling nervous about sexual performance, known as Sexual Performance Anxiety (SPA), is pretty common. But…
Commitment issues can often manifest in romantic relationships, work, and other personal or professional spheres.…
Table of Contents
ToggleDr. Russell Wilder developed the ketogenic – or “keto” – diet as early as 1924 to treat epilepsy in his patients effectively. The diet aims to accomplish weight loss by burning fat, emphasizing high-fat and low-carb intake. The goal of the keto diet is to quickly shed weight without hunger or cravings, with proponents claiming it can boost mood, improve mental focus, and increase energy.
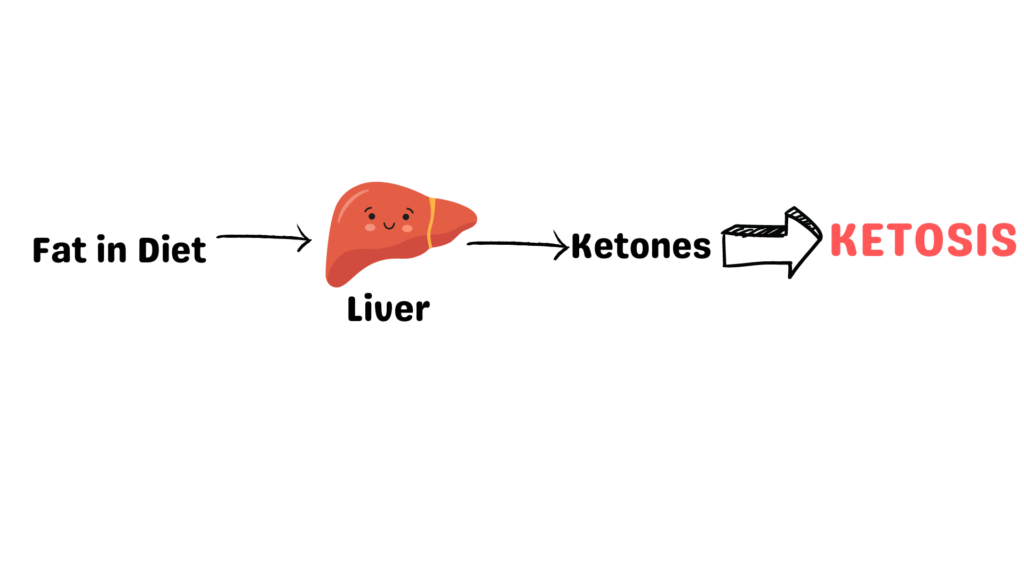
On the ketogenic diet, individuals consume minimal carbohydrates or sugar. Instead of relying on carbohydrates and sugars (glucose) as its primary source of fuel, the body shifts to using ketones. Ketones, a byproduct produced when the liver begins burning fat, serve as an alternative energy source when glucose is unavailable.
This dietary approach is not meant for long-term use but rather as an intermittent strategy for sustained weight loss. After a few months on keto, reintroducing smaller portions of carbohydrates becomes necessary to restart the process of ketosis.
This diet emphasizes limited carbohydrate and sugar intake, moderate protein consumption, and high fat intake. Excessive protein intake is discouraged as the body can convert excess protein into glucose, hindering or delaying the achievement of ketosis.
Several versions of the ketogenic diet exist, and the type of diet you follow determines your food intake. These versions include:
This diet features very low carbohydrate, moderate protein, and high fat intake. Typically, it comprises 70% fat, 20% protein, and only 10% carbohydrates.
This diet involves alternating periods of high carbohydrate intake. Such as 5 days of following a ketogenic regimen followed by 2 days of high carbohydrate intake.
With this diet, individuals can incorporate carbohydrates around their workout sessions.
Similar to the standard ketogenic diet, this variant includes higher protein intake. The typical ratio is 60% fat, 35% protein, and 5% carbohydrates.
Extensive research has primarily focused on the standard and high-protein ketogenic diets. Cyclical or targeted ketogenic diets are considered more advanced methods and are predominantly utilized by bodybuilders or athletes.
Research suggests that the ketogenic diet can effectively promote short-term weight loss. However, in the long run, it may not offer significant advantages over low-fat diets that permit higher carbohydrate intake.
Initially, weight loss on the ketogenic diet primarily stems from the depletion of glycogen stores, which results in the loss of associated water weight through increased urination or sweating.
A review of 53 clinical trials found that individuals following keto-type diets experienced greater weight loss and more favorable health outcomes compared to those on calorie-counting, low-fat diets. Researchers concluded that low-carb, high-fat diets composed of unprocessed, whole foods represent a viable, effective, and safe approach to weight loss.
Reports from peer-reviewed medical education studies indicate that individuals on the ketogenic diet may experience rapid initial weight loss of up to 10 pounds within two weeks or less.
Due to its highly restrictive nature, experts do not recommend the ketogenic diet for long-term weight maintenance and management. This approach may result in deficiencies of essential vitamins and nutrients.
Diabetes involves metabolic changes, high blood sugar levels, and impaired insulin function.
The ketogenic diet can aid in shedding excess fat, which is closely associated with type 2 diabetes, prediabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
In a small study involving women with type 2 diabetes, adherence to a ketogenic diet for 90 days led to a significant reduction in hemoglobin A1C (HbA1c) levels, indicative of improved long-term blood sugar management.
Research has indicated that the ketogenic diet offers benefits for various health conditions:
However, it’s important to note that research in many of these areas is still inconclusive.
Limiting or eliminating high-carb foods is crucial on a ketogenic diet. Here’s a list of foods that should be reduced or eliminated:
The foundation of your meals should primarily consist of the following foods:
To begin, stocking the pantry with keto-friendly foods is essential. These include herbs and spices, low-carb flours like almond flour, sweeteners such as stevia, canned sardines and tuna, tea, coffee, starch substitutes like cauliflower rice, and low-carb noodles.
Maintaining a food diary can be beneficial for adhering to the keto regimen. Utilizing an app to track daily food consumption is recommended. This practice helps individuals determine if they are consuming the appropriate foods and macronutrient ratios to induce ketosis effectively.
Additionally, ketone urine strips or blood test monitors can aid in monitoring one’s state of ketosis. Food diaries also facilitate tracking any symptoms that may arise or progress while following a new dietary regimen.
To assist you in getting started, here’s a sample ketogenic diet meal plan for one week:
Always aim to rotate vegetables and meat over the long term to ensure a variety of nutrients and health benefits.
While the ketogenic diet offers benefits, adhering to it in the long term may pose certain risks, including:
Further research is underway to evaluate the long-term safety of the diet. It’s advisable to keep your doctor informed about your dietary choices to receive appropriate guidance.
Before embarking on the ketogenic diet, it’s imperative to ensure that you are medically suitable to follow it without encountering adverse effects. The best approach to verify your suitability for the ketogenic diet is to consult with your doctor.
Avoid adopting the ketogenic diet if you fall into any of the following categories:
Expectant and nursing mothers require an increased intake of nutrients. Restricting your diet, as the ketogenic diet does, can lead to complications for both you and your developing baby.
If you manage your diabetes through regular insulin injections, drastically reducing your carbohydrate intake may result in dangerously low blood glucose levels, leading to further health complications. It’s crucial to discuss with your doctor to determine the best approach to initiating the ketogenic diet in this scenario.
If you have a history of yo-yo dieting and crash diets, you may struggle to maintain adherence to the ketogenic diet consistently. Achieving and sustaining ketosis, the cornerstone of the diet’s effectiveness requires consistent commitment over several months, which may be challenging if you’re accustomed to erratic dieting patterns.
Epileptic children following the ketogenic diet have demonstrated a heightened risk of compromised bone health. While the reasons are not fully understood, it’s advisable to refrain from the diet if you have a family history of osteoporosis, increasing your susceptibility to the condition.
The ketogenic diet, being low in fiber due to its exclusion of whole wheat and most whole grains, can exacerbate digestive problems such as chronic constipation or IBS. Additionally, fiber is essential for nourishing the gut microbiome, a crucial component of physical and mental well-being. If you are genetically predisposed to an imbalanced microbiome, it’s prudent to avoid the diet.
Some individuals experience challenges in digesting fats, which can pose a significant obstacle to a fat-dependent diet like keto. Factors contributing to difficulty in fat digestion include surgical removal of the gallbladder, fatty liver disease, inadequate bile production by the liver, or blocked bile ducts causing bile congestion. If your doctor deems the ketogenic diet beneficial for you, they may prescribe nutrients to facilitate fat digestion and absorption.
While adhering to the keto diet, you lower your carbohydrate intake and substitute it with healthy fats. This shift can prompt your body to utilize fat for energy, facilitating weight loss and potentially lowering the risk of developing certain health conditions.
However, it’s essential to consult your doctor before committing to the diet for an extended duration, as it may entail some side effects. Further research is required to comprehend its long-term impact on the body.
References
Dr. Nishtha, a medical doctor holding both an MBBS and an MD in Biochemistry, possesses a profound passion for nutrition and wellness. Her personal journey, marked by significant struggles with physical and mental health, has endowed her with a unique empathy and insight into the challenges countless individuals face. Driven by her own experiences, she leverages her background to offer practical, evidence-backed guidance, empowering others on their paths to achieving holistic well-being. Dr. Nishtha truly believes in the interconnectedness of the mind and body. She emphasizes the significance of understanding this connection as a crucial stride toward attaining balance and happiness in life.