Discover comprehensive information for all aspects of sexual health and find resources and guidance to empower your sexual well-being.
The underlying cause as well as the severity of pain determine the varied treatment approaches…
Discover comprehensive information for all aspects of sexual health and find resources and guidance to empower your sexual well-being.
The underlying cause as well as the severity of pain determine the varied treatment approaches…
Feeling nervous about sexual performance, known as Sexual Performance Anxiety (SPA), is pretty common. But…
Painful erections never indicate normalcy, and sometimes signal a medical emergency. Severe pain may necessitate…
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a condition that affects many men worldwide, leading to significant stress,…
Sleep-related painful erection (SRPE) is a rare condition where people get painful erections while they’re…
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition affecting men, often characterized by the inability to…
Commitment issues can often manifest in romantic relationships, work, and other personal or professional spheres.…
Sigmund Freud’s renowned theory of personality suggested that the human psyche comprises three distinct yet interconnected elements – the id, the ego, and the superego. This tripartite model explains the complexities of human behavior and mental processes. It illustrates the dynamic interactions between instinctual drives, reality, and moral standards.
The three parts develop at different stages in our lives and play unique roles in personality. But they work together to form a whole and contribute to an individual’s behavior.
Table of Contents
ToggleFreud’s psychoanalytic theory states that the id is the primal and instinctual part of the psyche. The id harbors sexual and aggressive impulses as well as concealed memories. The super-ego acts as a moral compass. The ego functions as the practical component. It negotiates between the id’s impulses and the super-ego’s ethical considerations.
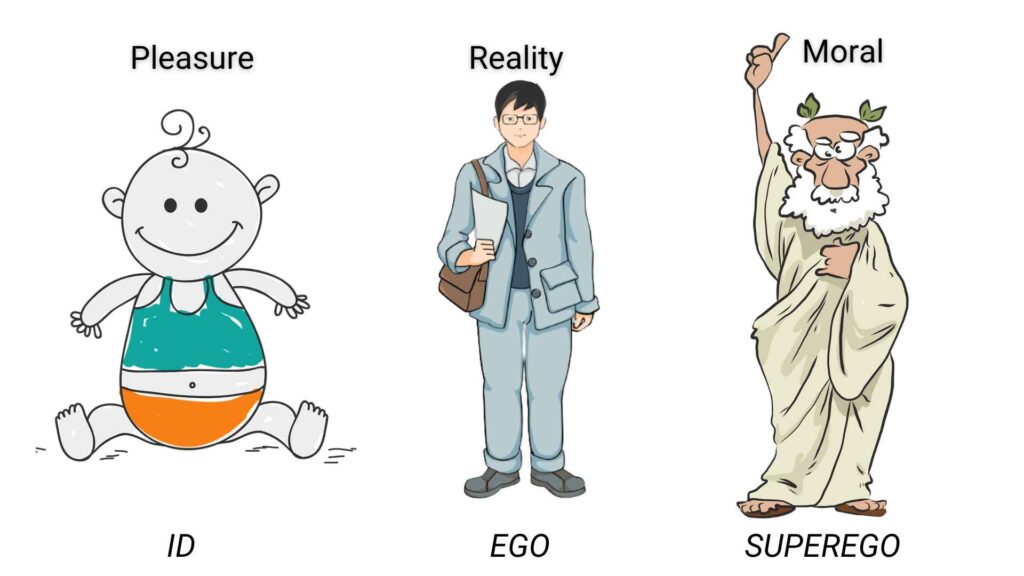
The earliest part of the personality to manifest is the id.
The id is present at birth and runs purely on wants and desires. It exists in our unconscious mind and represents our biological, instinctual urges.
Newborns have a fully developed Id, which drives them to seek out their basic needs, such as food, in order to survive.
Motivated solely by the pleasure principle (i.e., “if it feels good, do it”), the id operates stubbornly, and any unfulfilled desires result in tension.
Freud held the view that our most fundamental nature is as primal as that of any animal, with basic impulses such as hunger, thirst, aggression, and lust.
Being an unconscious entity, the Id remains in an infantile state, devoid of any consideration for reality, and behaves irrationally. The ego and superego emerge to restrain and regulate the id’s behavior.
The Superego develops during the phallic stage of Freud’s psychosexual development between the ages of 3 and 5. It primarily resides in our unconscious mind but has the ability to influence our conscious thoughts.
It encompasses the moral principles we learn during childhood, including values, rules, and expectations absorbed from our society, culture, and family, and it maintains a sense of morality.
The Superego comprises two essential elements: the conscience and the ideal self.
It serves as our “inner voice,” which informs us when we have done something wrong and punishes us through feelings of guilt and shame.
On the other hand, the ideal self establishes the rules and standards of proper behavior we should follow as members of society, rewarding good conduct with feelings of pride.
For example, a student forgets to study for a test and feels tempted to cheat off a neighboring student. Even though the chances of getting caught are slim, the Superego would suppress the urge to cheat because it recognizes that it is wrong.
According to Freud, the Ego represents our conscious self and acts as the mediator between the impulses of the Id and the moral reasoning of the Superego.
The Ego develops from the Id and ensures that its impulses are expressed in socially acceptable ways, guided by the “reality principle.”
This principle prompts the Ego to find realistic solutions to satisfy the Id’s desires while functioning within society’s norms and rules, such as through delaying gratification or compromise.
The Ego’s rational thinking, called secondary process thinking, enables problem-solving and reality-testing, helping the individual maintain self-control. However, like the Id, the Ego also seeks pleasure but in a realistic manner, not concerned with morality but focused on maximizing pleasure and minimizing pain while avoiding negative consequences.
Freud’s analogy of the id as a horse and the ego as the rider illustrates the Ego provides direction and guidance, just as the rider controls the horse’s movements. Without the Ego’s influence, the Id would wander aimlessly and act upon its impulses without regard for social conventions.
According to Freud, the unconscious mind contains the Id and the Superego, which are constantly at odds with each other as they vie for influence over the conscious mind’s Ego.
A psychologically balanced individual is capable of moderating the impacts of the Id and Superego.
At the same time, an unhealthy person may experience an overactive Id or Superego that they are unable to satisfy. This leads to mental health issues such as anxiety.
The Id and Superego are frequently depicted as the classic angel and devil on cartoon characters’ shoulders, with the Ego becoming vulnerable and confused if one holds more sway than the other.
These ongoing internal struggles cause us to experience tension and angst, resulting in anxiety that can be assuaged by defense mechanisms. Freud described defense mechanisms as the subconscious thoughts and behaviors we utilize to alleviate the conflict between the Id and the Superego.
Related: Defense Mechanisms: All You Need To Know
Freud’s model of the tripartite personality has significant clinical implications. Understanding the id, ego, and superego provides insights into various psychological disorders and informs therapeutic approaches in psychoanalysis.
Freud’s tripartite model of the id, ego, and superego offers a comprehensive framework for understanding the complexities of human behavior and mental processes. By examining the interactions and conflicts between these three components, we gain valuable insights into the dynamics of personality and the roots of psychological distress.
Dr. Nishtha, a medical doctor holding both an MBBS and an MD in Biochemistry, possesses a profound passion for nutrition and wellness. Her personal journey, marked by significant struggles with physical and mental health, has endowed her with a unique empathy and insight into the challenges countless individuals face. Driven by her own experiences, she leverages her background to offer practical, evidence-backed guidance, empowering others on their paths to achieving holistic well-being. Dr. Nishtha truly believes in the interconnectedness of the mind and body. She emphasizes the significance of understanding this connection as a crucial stride toward attaining balance and happiness in life.