Discover comprehensive information for all aspects of sexual health and find resources and guidance to empower your sexual well-being.
The pelvic floor muscles are the unsung heroes of our body’s core, providing support to…
Discover comprehensive information for all aspects of sexual health and find resources and guidance to empower your sexual well-being.
The pelvic floor muscles are the unsung heroes of our body’s core, providing support to…
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a condition that affects many men worldwide, leading to significant stress,…
The underlying cause as well as the severity of pain determine the varied treatment approaches…
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition affecting men, often characterized by the inability to…
Prostate health is a critical concern for men, especially as they age. The prostate gland…
Feeling nervous about sexual performance, known as Sexual Performance Anxiety (SPA), is pretty common. But…
Commitment issues can often manifest in romantic relationships, work, and other personal or professional spheres.…
Your body’s metabolism controls how it uses energy from the food you consume, but the food itself can also influence the process. Choosing foods high in protein and fiber helps your body avoid storing fat and increases its energy utilization. Additionally, controlling when and how much you eat can impact your metabolic rate.
While eating less might appear beneficial for dieting, consuming too little food can be more harmful than eating too much.
Dieting involves consuming fewer calories than your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR), but consuming too few signals to your body that you’re starving, prompting it to reduce energy expenditure and store excess fat.
Here are a few ways proven to boost metabolism.
Table of Contents
ToggleThere are no magical foods that will instantly provide you with the perfect metabolism in a short period.
However, certain foods do possess superior energy balance properties. They aid the body in converting calories into usable energy rather than storing them as fat.
It’s important to note that not all metabolism-boosting foods suit everyone. If you’re aware of any allergies or sensitivities to particular products, eliminate them from your list and explore alternative options.

Caffeine stimulates the central nervous system, triggers hormone secretion, and alters biochemical and physiological parameters. It regulates fat metabolism and also modulates glucose metabolism.
Studies have demonstrated that caffeine, present in coffee, chocolate, and various other products, enhances performance during high-intensity exercise.
A Japanese study suggested that drinking a single cup of brewed tea per day could increase metabolism by up to 12 percent, attributed to the additional antioxidants present in this beverage.

Capsaicin, the compound that’s responsible for making peppers spicy, is also known for improving metabolism.
Recent research has revealed the association between capsaicin and the composition, abundance, and function of gut microbiota, shedding light on the potential mechanisms through which capsaicin exerts its influence.

If you primarily consume warm or hot beverages, they could potentially contribute to metabolic issues. Replacing these drinks with cold water can elevate your resting metabolic rate by up to 50 calories per day when consuming 48 ounces (1.4 liters).
Additionally, staying hydrated with water helps ensure you burn approximately 2 percent more calories compared to when your body is dehydrated.
Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and tuna are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been associated with various health benefits, including metabolic regulation.
Omega-3 fatty acids may help enhance insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and promote fat metabolism, all of which can contribute to improved metabolic function.

Most fruits and vegetables contain high levels of fiber, making them an excellent way to reduce appetite. They also boost fat-burning potential, similar to whole grains, particularly when aiming for a daily intake of 25 to 30 grams of fiber.

Iron plays a crucial role in the body’s metabolism by aiding in the production of energy from nutrients and supporting various metabolic processes.
When the body has sufficient iron levels, it can effectively metabolize carbohydrates, fats, and proteins for energy production. Including iron-rich foods such as lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, tofu, and fortified cereals in your diet can help support a healthy metabolism.
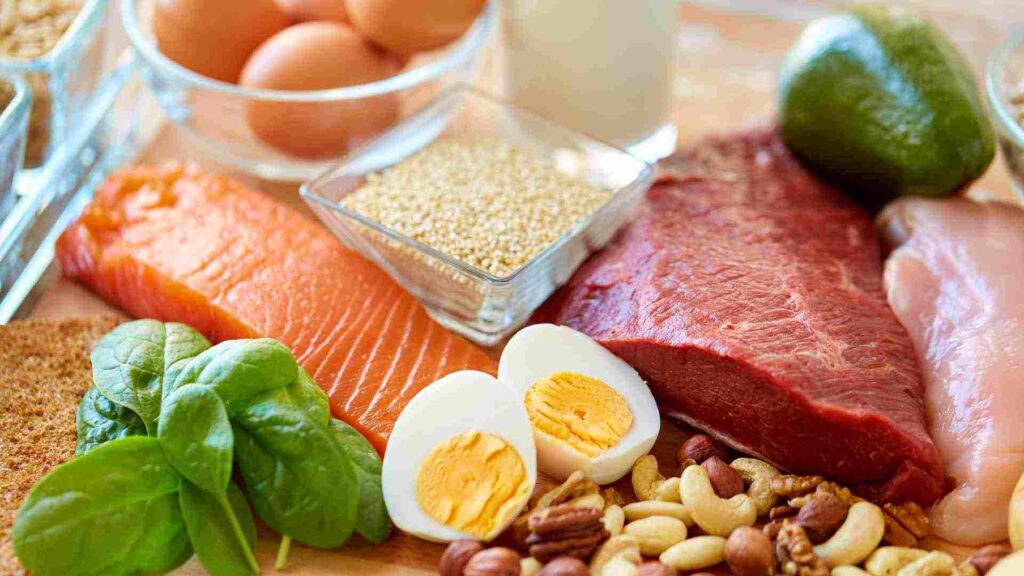

Proteins are essential nutrients that play a significant role in metabolism. They require more energy to digest compared to fats or carbohydrates, a process known as the thermic effect of food (TEF). This means that consuming protein-rich foods can temporarily boost metabolism by increasing the number of calories burned during digestion.
Furthermore, protein helps support muscle growth and maintenance. Since muscle tissue is metabolically active and requires energy even at rest, having more muscle mass can contribute to a higher resting metabolic rate. Therefore, including lean protein sources such as chicken breast, turkey, fish, tofu, beans, lentils, and low-fat dairy products in your diet can help enhance metabolism and support overall health and weight management.
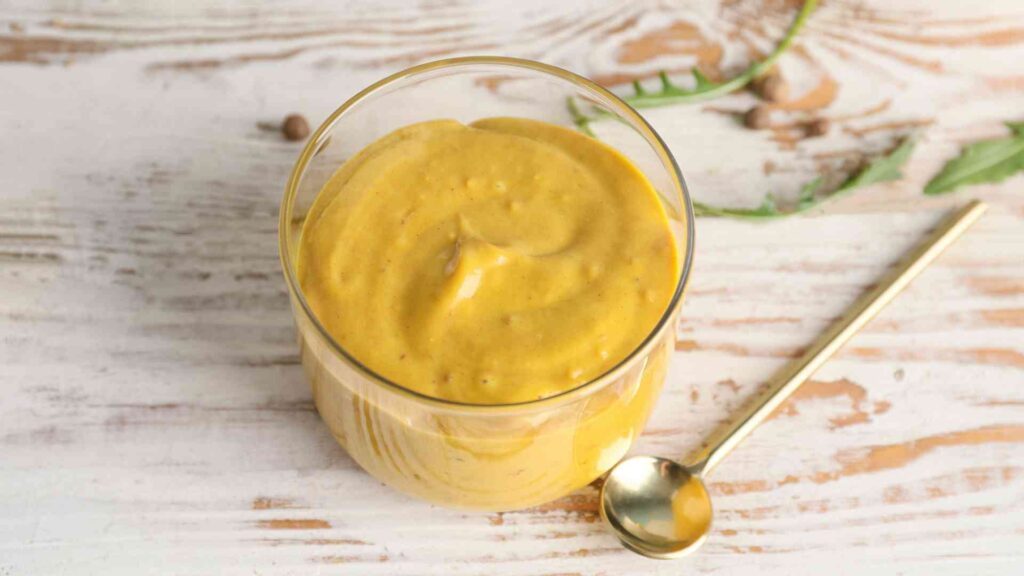

Some research suggests that mustard may help to stimulate metabolism and promote fat burning. However, the evidence is limited and more research is needed to fully understand the effects.
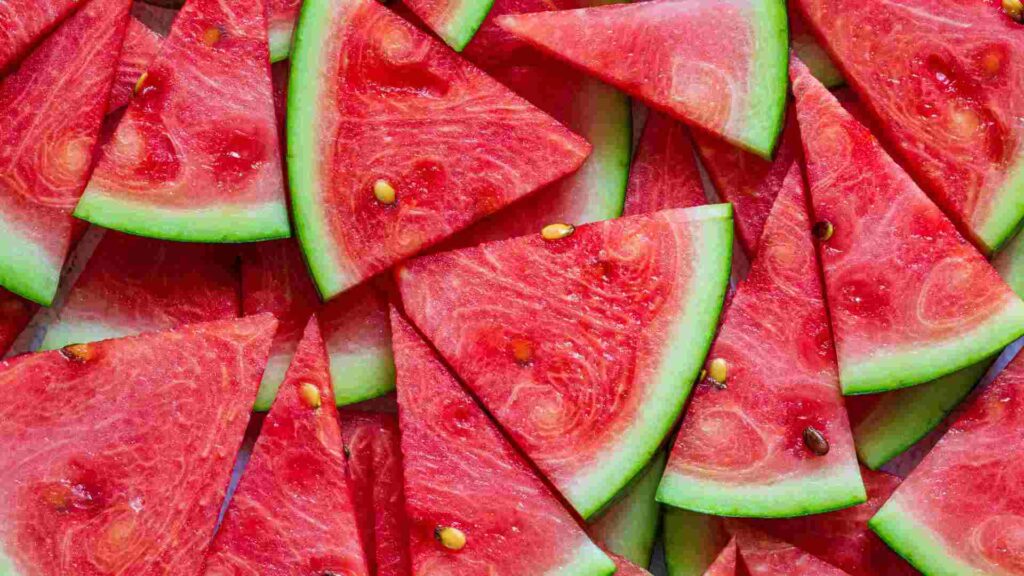

Watermelon is a hydrating and low-calorie fruit that contains various vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. While there is no direct evidence to suggest that watermelon specifically improves metabolism, staying hydrated by consuming water-rich foods like watermelon can support overall metabolic function.
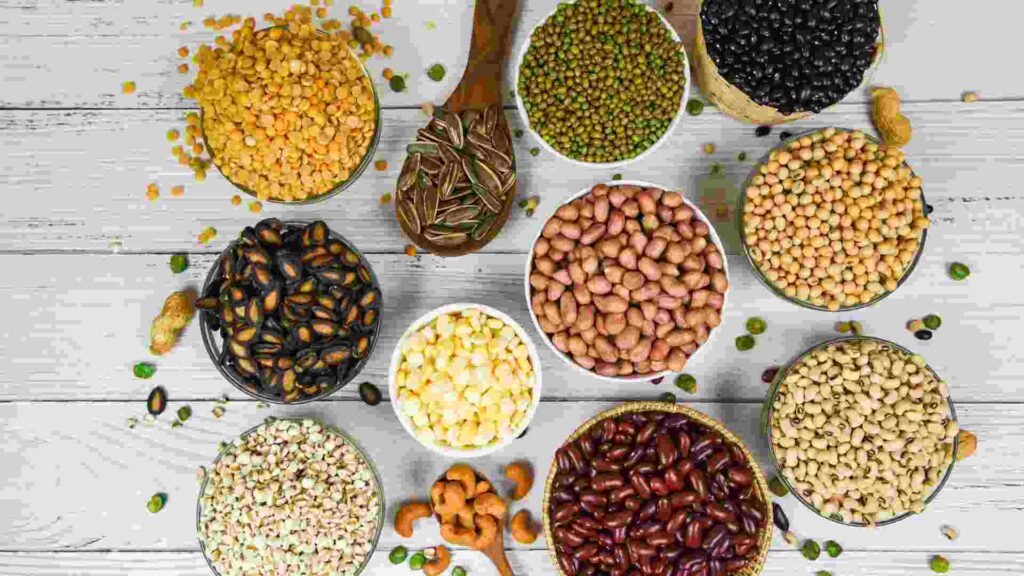

Whole grains, such as oats, brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat, are rich in complex carbohydrates, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. These nutrients play important roles in metabolic processes within the body.
Some research suggests that the consumption of whole grains may have a modest effect on increasing resting metabolic rate due to their complex structure and the energy required for digestion.

It can potentially improve metabolism due to its nutrient composition and probiotic content.
Yogurt is a good source of protein, which is important for muscle maintenance and repair. Since muscle tissue is metabolically active, having adequate protein intake can support a healthy metabolism by preserving lean muscle mass.
It also helps maintain a healthy balance of gut microbiota, which plays a role in digestion and metabolism.
Yogurt is also rich in calcium, which is important for bone health but may also have metabolic benefits. Calcium has been suggested to play a role in fat metabolism, and adequate calcium intake may help regulate body weight and fat storage.

Ginger may have a modest effect on boosting metabolism. It contains compounds like gingerol and capsaicin, which have been studied for their potential thermogenic (heat-producing) effects and their ability to increase calorie expenditure.
Additionally, ginger has been shown to aid in digestion and reduce appetite, which could indirectly support metabolic function. However, more research is needed to fully understand the extent of ginger’s impact on metabolism.

Regular exercise is one of the most important things you can do to improve your metabolism. Every kind of exercise counts, from light walking to strength training to vigorous aerobic activity.

When you consume alcohol, your body prioritizes metabolizing it over other nutrients. Unlike proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, which are broken down and used for energy, alcohol is processed by the liver into acetate, which the body can use as fuel.
During this process, the metabolism of other nutrients is temporarily halted, leading to a slowdown in the overall metabolic rate. Additionally, excess alcohol consumption can lead to liver damage, further impacting metabolism.
Furthermore, alcoholic beverages often contain empty calories with little to no nutritional value, which can contribute to weight gain and interfere with weight loss efforts if consumed excessively.

Poor sleep quality can contribute to a slower metabolism.
Sleep deprivation disrupts the balance of hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism.
When you’re sleep-deprived, you may feel fatigued and have less energy for physical activity, resulting in fewer calories burned throughout the day.
Lack of sleep can activate the body’s stress response system, leading to increased levels of stress hormones like cortisol. Chronically elevated cortisol levels can promote fat storage, particularly around the abdomen, and negatively impact metabolism.
Irregular sleep patterns and shift work have been associated with metabolic disturbances and an increased risk of metabolic disorders such as obesity and type 2 diabetes.

Stress can lead to a slower metabolism due to elevated cortisol levels, muscle loss, insulin resistance, and disrupted eating patterns. Chronic stress can contribute to metabolic disturbances, increasing the risk of weight gain and metabolic disorders.
Boosting metabolism involves several key steps. Focus on consuming protein-rich foods, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular physical activity. Ensure you get adequate sleep and include metabolism-boosting foods like whole grains, fatty fish, and fruits and vegetables in your diet. Manage stress levels and limit alcohol intake, while also practicing portion control and mindful eating. These strategies can help support a healthy metabolism and overall well-being.
References
Dr. Nishtha, a medical doctor holding both an MBBS and an MD in Biochemistry, possesses a profound passion for nutrition and wellness. Her personal journey, marked by significant struggles with physical and mental health, has endowed her with a unique empathy and insight into the challenges countless individuals face. Driven by her own experiences, she leverages her background to offer practical, evidence-backed guidance, empowering others on their paths to achieving holistic well-being. Dr. Nishtha truly believes in the interconnectedness of the mind and body. She emphasizes the significance of understanding this connection as a crucial stride toward attaining balance and happiness in life.

