Discover comprehensive information for all aspects of sexual health and find resources and guidance to empower your sexual well-being.
Prostate health is a critical concern for men, especially as they age. The prostate gland…
Discover comprehensive information for all aspects of sexual health and find resources and guidance to empower your sexual well-being.
Prostate health is a critical concern for men, especially as they age. The prostate gland…
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a condition that affects many men worldwide, leading to significant stress,…
The underlying cause as well as the severity of pain determine the varied treatment approaches…
Painful erections never indicate normalcy, and sometimes signal a medical emergency. Severe pain may necessitate…
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition affecting men, often characterized by the inability to…
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition that affects men of all ages, impacting their…
Commitment issues can often manifest in romantic relationships, work, and other personal or professional spheres.…
Vitamin D deficiency (VDD) has emerged as a global problem over the last decade. Undiagnosed vitamin D deficiency is also quite common.
Table of Contents
ToggleVit D is a fat-soluble vitamin which is sometimes called the sunshine vitamin because our body makes it from cholesterol when our skin is exposed to sunlight.

Vitamin D plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of calcium in your blood and bones and building and maintaining bones.
Specifically, your body needs vit D to utilize calcium and phosphorus for bone-building and tissue support.
Chronic and/or severe vitamin D deficiency causes a decline in calcium and phosphorus absorption by your intestines, resulting in hypocalcemia (low calcium levels in your blood) and secondary hyperparathyroidism (overactive parathyroid glands attempting to regulate blood calcium levels).
Symptoms such as muscle weakness, cramps, fatigue, and depression may occur due to both hypocalcemia and hyperparathyroidism if they are severe.
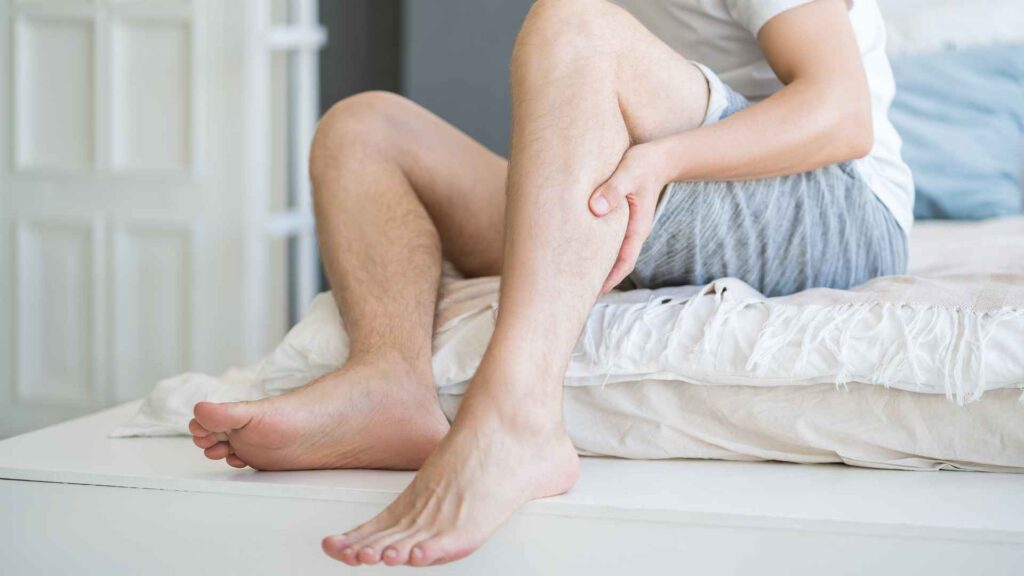

To address low calcium levels in your blood through secondary hyperparathyroidism, your body withdraws calcium from your bones, leading to accelerated bone demineralization (the breakdown of bones surpasses their formation). This process can result in osteomalacia (soft bones) in adults and rickets in children.
It may even help prevent cancer and protect against several chronic conditions, including

Humans get vit D from exposure to sunlight, from their diet, and dietary supplements.
Note: Because any excess Vit D is destroyed by sunlight, excessive exposure to sunlight does not cause vitamin D toxicity
Vit D deficiency occurs when we don’t have enough of it in our body.
Although there is no consensus on optimal vit D levels in blood, deficiency is generally diagnosed at blood levels of <12 ng/mL. A level of >20 ng/mL is considered sufficient. ≥12-20 ng/mL of Vitamin D is insufficient.
Causes of deficiency are:

This occurs due to sunscreen use, covered clothing, skin pigmentation, skin grafts, and aging.
Note: Darker skin may not get enough vit D through sunlight.
This can occur in disorders of absorption of dietary Vit D (Malabsorption), bypass surgery, and obesity.
The kidney is involved in the activation of Vit D. Patients with kidney disease also have vit D deficiency.
The Liver is involved in Vitamin D formation, and liver failure leads to deficiency.
Certain genetic diseases of Vit D metabolism lead to its deficiency.
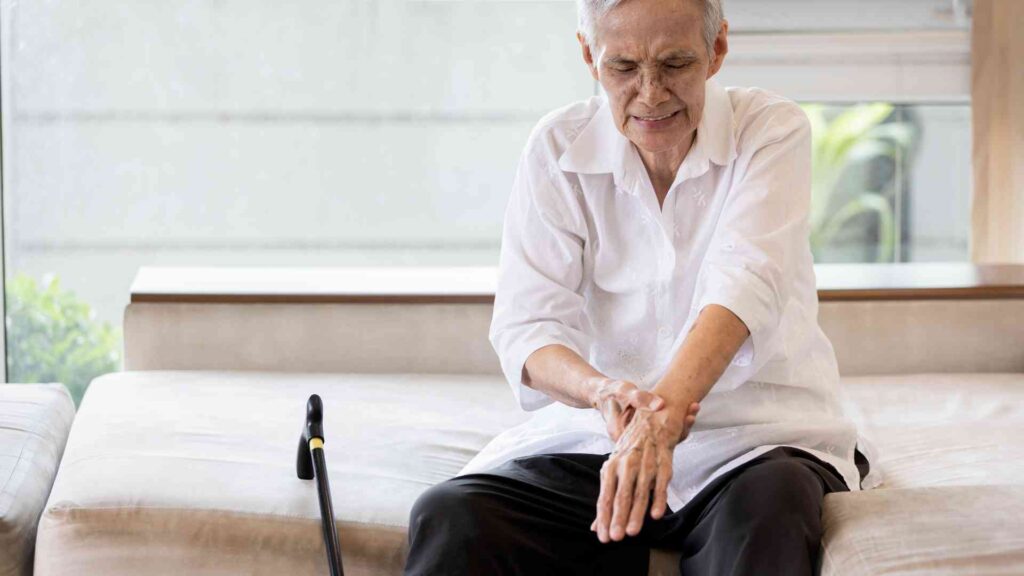

Osteomalacia happens when bones in adults don’t get enough minerals to stay strong as they naturally replace old bone tissue with new. This leads to a gradual loss of minerals from the bones, even though the bone structure itself is okay.
The result? Painful bones, misshapen skeletons, and weaker muscles.
Women who don’t get enough vit D, especially after having several pregnancies, are more likely to develop osteomalacia. This is because their bodies have to use up a lot of calcium to help their babies grow strong bones before birth and to produce milk for breastfeeding.
Elderly people are also at risk of osteomalacia. As people age, their skin makes less of a substance called 7-dehydrocholesterol, which the body uses to produce vitamin D when exposed to sunlight. Plus, many older adults don’t spend as much time in the sun, which means they may not get enough vitamin D to keep their bones healthy.

Rickets is a condition that affects young children and adolescents when their bones don’t get enough minerals to become strong. In babies, this means that the soft cartilage at the ends of bones keeps growing but doesn’t harden into proper bone. One early sign of rickets is a soft spot on the baby’s head that takes longer to close up than usual.
As rickets progresses, the ends of bones can swell up, especially where the ribs meet the cartilage. This can make the ribcage look like it has beads on it, which is called a “rachitic rosary.” In severe cases, this can even cause the chest to cave in, making it hard to breathe.
When a child with rickets starts to walk, their weight can bend their soft bones, leading to bowed legs or knees that knock together. This can also affect the shape of the pelvis. Similar bone problems can happen during the teenage growth spurt.
In very severe cases, not having enough calcium in the blood can cause muscle spasms called tetany because the body can’t maintain the right balance of minerals inside cells.

Adequate daily intake of vitamin D is:
Treatment of Vit D Deficiency is by oral or injectable Vit D supplementation along with oral calcium supplementation. The duration and dosage depend on the clinical condition and the severity of the deficiency.
A blood level of >100 ng/mL defines vit D toxicity which might occur due to excessive supplementation. This may cause increased blood levels of calcium in blood and urine.
Vitamin D deficiency occurs surprisingly commonly, but its symptoms are often subtle and nonspecific, making it difficult to determine whether one has a deficiency or another health condition. If you suspect a deficiency, consult a healthcare professional for a blood test. Treatment for deficiency typically involves supplements and dietary and lifestyle adjustments.
References
Dr. Nishtha, a medical doctor holding both an MBBS and an MD in Biochemistry, possesses a profound passion for nutrition and wellness. Her personal journey, marked by significant struggles with physical and mental health, has endowed her with a unique empathy and insight into the challenges countless individuals face. Driven by her own experiences, she leverages her background to offer practical, evidence-backed guidance, empowering others on their paths to achieving holistic well-being. Dr. Nishtha truly believes in the interconnectedness of the mind and body. She emphasizes the significance of understanding this connection as a crucial stride toward attaining balance and happiness in life.

